Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Compute and plot 2D streamlines#
This example shows you how to compute and plot streamlines of fluid simulation results, for 2D models.
Note
This example requires DPF 7.0 (ansys-dpf-server-2024-1-pre0) or above. For more information, see Compatibility.
Plot surface streamlines#
Import modules, create the data sources and the model#
Import modules:
from ansys.dpf import core as dpf
from ansys.dpf.core import examples
from ansys.dpf.core.helpers.streamlines import compute_streamlines
from ansys.dpf.core.plotter import DpfPlotter
Create data sources for fluids simulation result:
fluent_files = examples.download_fluent_multi_species()
ds_fluent = dpf.DataSources()
ds_fluent.set_result_file_path(fluent_files["cas"], "cas")
ds_fluent.add_file_path(fluent_files["dat"], "dat")
Create model from fluid simulation result data sources:
m_fluent = dpf.Model(ds_fluent)
Get meshed region and velocity data#
Meshed region is used as the geometric base to compute the streamlines. Velocity data is used to compute the streamlines. The velocity data must be nodal.
Get the meshed region:
meshed_region = m_fluent.metadata.meshed_region
Get the velocity result at nodes:
velocity_op = m_fluent.results.velocity()
fc = velocity_op.outputs.fields_container()
field = dpf.operators.averaging.to_nodal_fc(fields_container=fc).outputs.fields_container()[0]
Compute single streamline#
single_2d_streamline, single_2d_source = compute_streamlines(
meshed_region=meshed_region,
field=field,
start_position=(0.005, 0.0005, 0.0),
surface_streamlines=True,
return_source=True,
)
Plot single streamline#
pl_single = DpfPlotter()
pl_single.add_field(field, meshed_region, opacity=0.2)
pl_single.add_streamlines(
streamlines=single_2d_streamline,
source=single_2d_source,
radius=0.00002,
)
# Use the PyVista 'cpos' optional argument to control the camera position.
# To easily save a camera position, plot the figure a first time with the argument
# 'return_cpos=True'. This will make the ``DpfPlotter.show_figure`` function return
# the camera position at the time the PyVista interactive plotting window is closed.
# You can also define a plane to use for the camera with 'cpos="xy"'.
# In this case the camera will fit the entire model in the window.
# Starting from a returned 'cpos', you can build a custom camera position, such as:
cpos = [
(0.005, 0.0004, 0.015), # Camera position (X, Y, Z)
(0.005, 0.0004, 0.0), # Target point (X, Y, Z)
(0.0, 1.0, 0.0), # Upward direction (+y)
]
return_cpos = pl_single.show_figure(return_cpos=True, cpos=cpos, show_axes=True)
print(return_cpos)
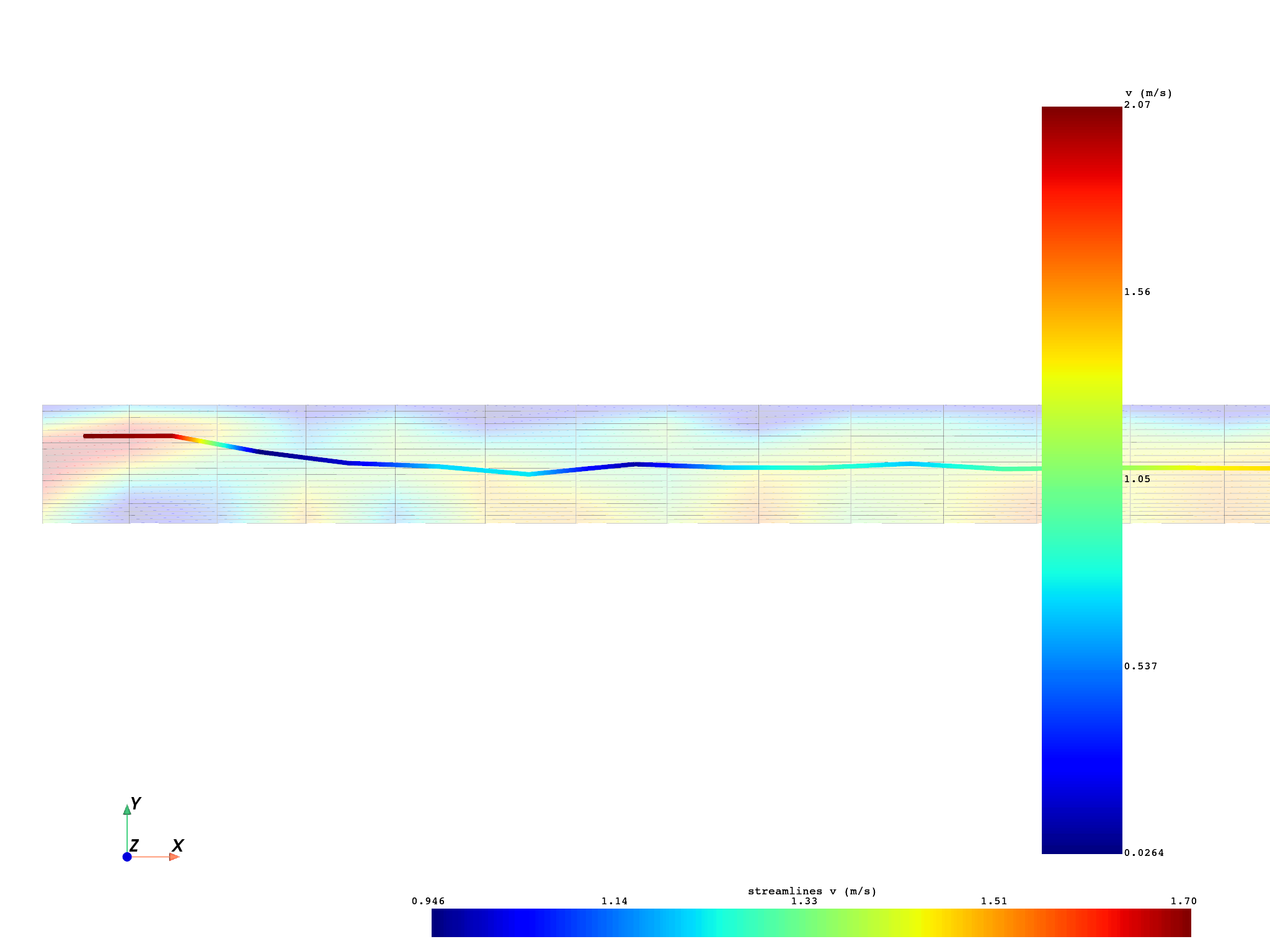
(CameraPosition(position=(0.005, 0.0004, 0.015),
focal_point=(0.005, 0.0004, 0.0),
viewup=(0.0, 1.0, 0.0)), <pyvista.plotting.plotter.Plotter object at 0x0000024EF9AD9550>)
Compute multiple streamlines#
multiple_2d_streamlines, multiple_2d_source = compute_streamlines(
meshed_region=meshed_region,
field=field,
pointa=(0.005, 0.0001, 0.0),
pointb=(0.005, 0.001, 0.0),
n_points=10,
surface_streamlines=True,
return_source=True,
)
Plot multiple streamlines#
pl_multiple = DpfPlotter()
pl_multiple.add_field(field, meshed_region, opacity=0.2)
pl_multiple.add_streamlines(
streamlines=multiple_2d_streamlines,
source=multiple_2d_source,
radius=0.000015,
)
pl_multiple.show_figure(cpos=cpos, show_axes=True)
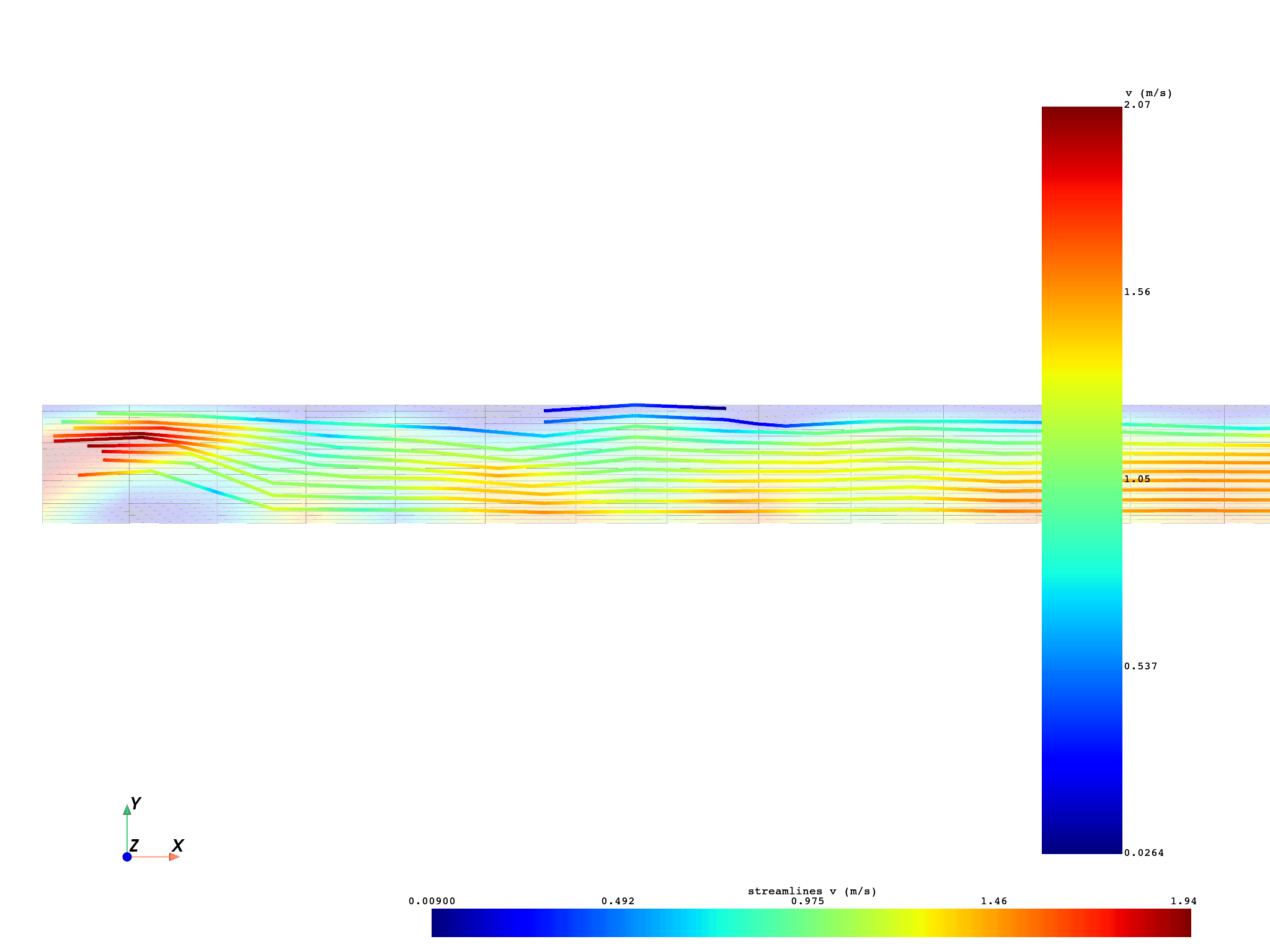
(None, <pyvista.plotting.plotter.Plotter object at 0x0000024EF9AD9D90>)
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 4.829 seconds)

