Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Compute iso-surfaces on fluid models#
This example demonstrates how to compute iso-surfaces on fluid models.
Note
This example requires DPF 7.0 (ansys-dpf-server-2024-1-pre0) or above. For more information, see Compatibility.
Import the dpf-core module and its examples files.#
import ansys.dpf.core as dpf
from ansys.dpf.core import examples
from ansys.dpf.core.plotter import DpfPlotter
Specify the file path.#
We work on a cas/dat.h5 file with only nodal variables.
path = examples.download_cfx_heating_coil()
ds = dpf.DataSources()
ds.set_result_file_path(path["cas"], "cas")
ds.add_file_path(path["dat"], "dat")
streams = dpf.operators.metadata.streams_provider(data_sources=ds)
Whole mesh scoping.#
We evaluate the mesh with the mesh_provider operator to scope the mesh_cut operator with the whole mesh.
whole_mesh = dpf.operators.mesh.mesh_provider(streams_container=streams).eval()
print(whole_mesh)
whole_mesh.plot()
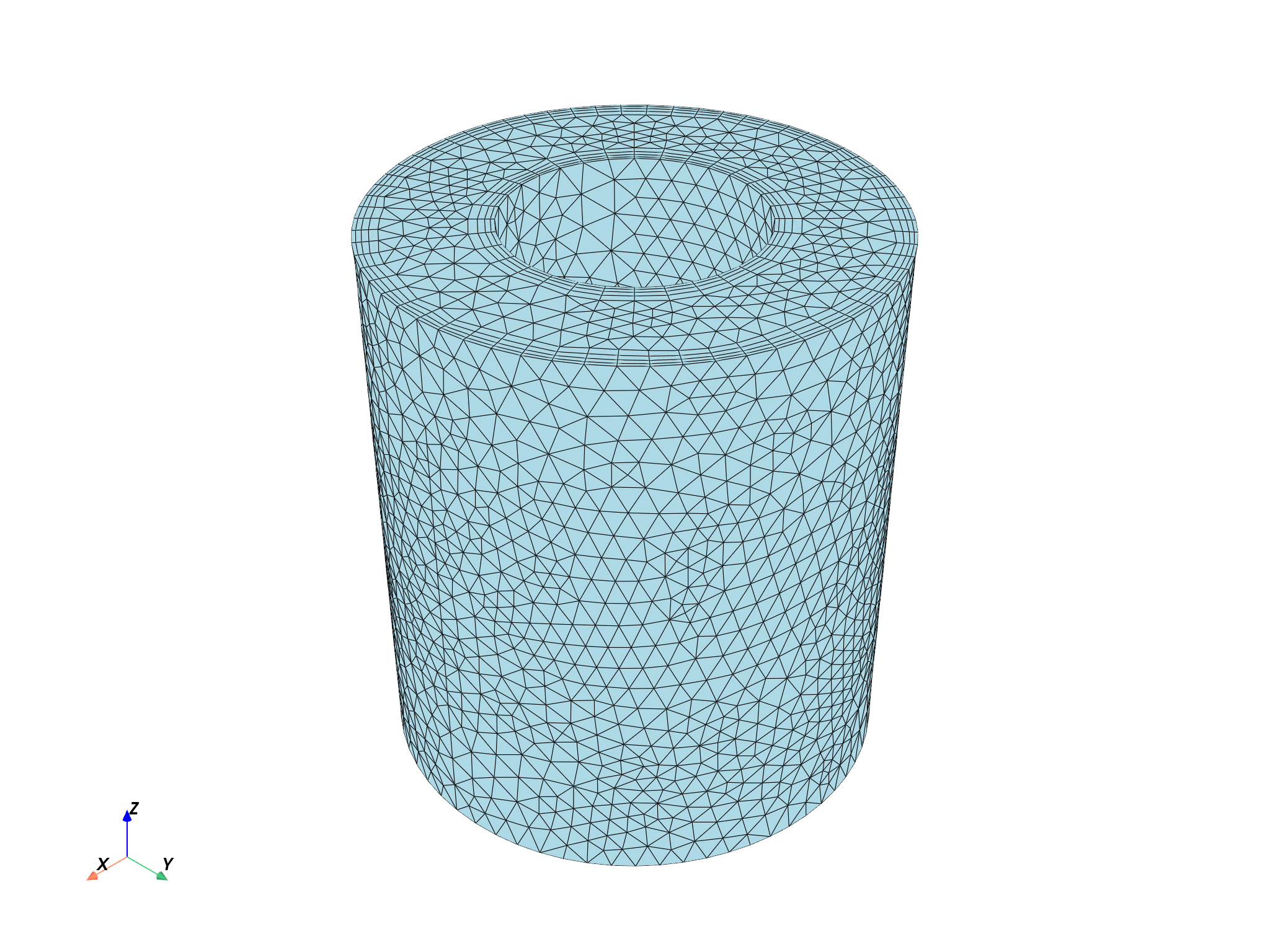
DPF Meshed Region:
25456 nodes
74882 elements
Unit: m
With solid (3D) elements
(None, <pyvista.plotting.plotter.Plotter object at 0x0000024EF9729610>)
Extract the physics variable#
Here we choose to work with the static pressure by default which is a scalar and nodal variable without multi-species/phases. With a multi-species case, select one using qualifier ellipsis pins and connecting a LabelSpace “species”/”phase”.
P_S = dpf.operators.result.static_pressure(streams_container=streams, mesh=whole_mesh).eval()
print(P_S[0])
pl = DpfPlotter()
pl.add_field(P_S[0])
cpos_mesh_variable = [
(4.256160478475664, 4.73662111240005, 4.00410065817644),
(-0.0011924505233764648, 1.8596649169921875e-05, 1.125),
(-0.2738679385987956, -0.30771426079547065, 0.9112125360807675),
]
pl.show_figure(cpos=cpos_mesh_variable, show_axes=True)
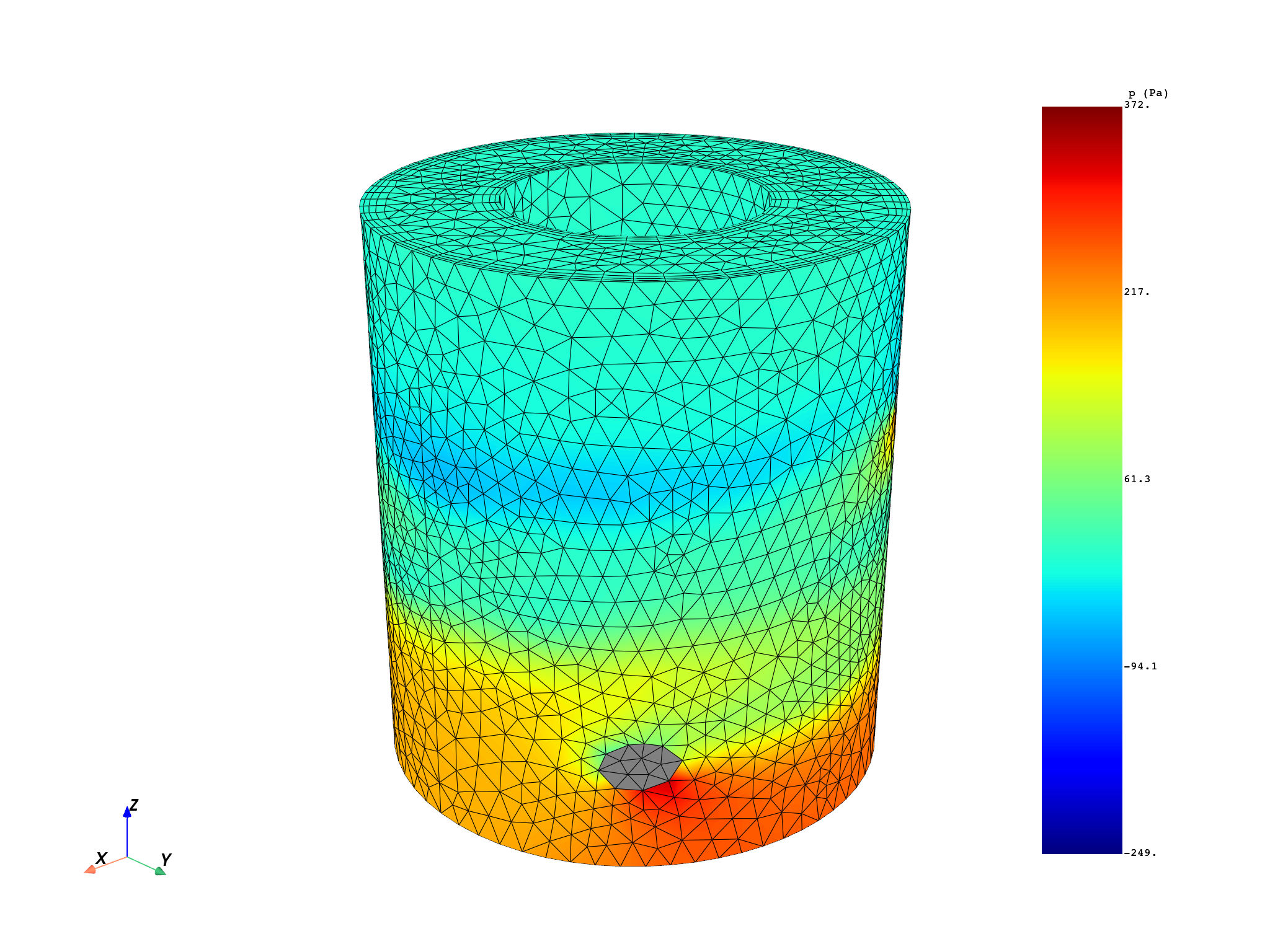
DPF p_<Mixture> Field
Location: Nodal
Unit: Pa
23648 entities
Data: 1 components and 23648 elementary data
Nodal
IDs data(Pa)
------------ ----------
1 6.804220e+01
2 -1.422350e+01
3 2.180406e+02
...
(None, <pyvista.plotting.plotter.Plotter object at 0x0000024EE99C3F90>)
Evaluate iso-surfaces#
We can finally use the iso_surfaces operator on this specific variable. We choose to cut the whole mesh with 9 iso-surface manually selected between the min and max of the static_pressure variable.
pl = DpfPlotter()
c_pos_iso = [
(4.256160478475664, 4.73662111240005, 4.00410065817644),
(-0.0011924505233764648, 1.8596649169921875e-05, 1.125),
(-0.2738679385987956, -0.30771426079547065, 0.9112125360807675),
]
pl.add_mesh(
meshed_region=whole_mesh,
style="wireframe",
show_edges=True,
show_axes=True,
color="black",
opacity=0.3,
)
vec_iso_values = [-153.6, -100.0, -50.0, 50.0, 100.0, 150.0, 200.0, 300.0, 361.8]
iso_surfaces_op = dpf.operators.mesh.iso_surfaces(
field=P_S[0], mesh=whole_mesh, slice_surfaces=True, vector_iso_values=vec_iso_values
)
iso_surfaces_meshes = iso_surfaces_op.outputs.meshes()
iso_surfaces_fields = iso_surfaces_op.outputs.fields_container()
for i in range(len(iso_surfaces_fields)):
pl.add_field(
field=iso_surfaces_fields[i],
meshed_region=iso_surfaces_meshes[i],
style="surface",
show_edges=False,
show_axes=True,
)
pl.show_figure(show_axes=True, cpos=c_pos_iso)
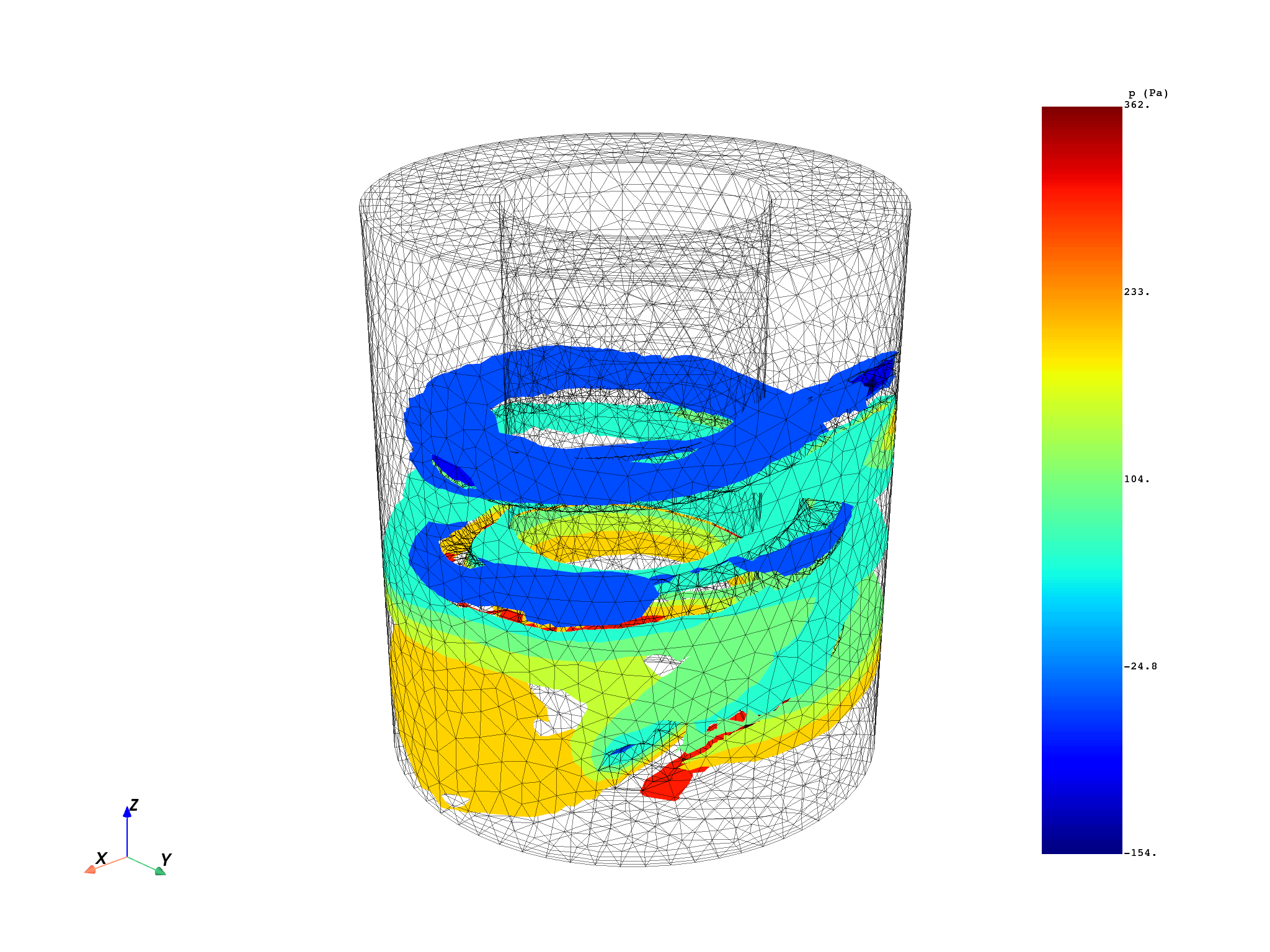
(None, <pyvista.plotting.plotter.Plotter object at 0x0000024EC6818AD0>)
Important note#
Iso-surfaces computation through the mesh_cut operator are only supported for Nodal Fields. For Elemental variables, you must perform an averaging operation on the Nodes before running the mesh_cut operator. This can be done by chaining the elemental_to_nodal operator output with the mesh_cut operator input.
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 5.940 seconds)

