Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Multi-stage cyclic symmetry using advanced customization#
This example shows how to expand on selected sectors the mesh and results from a multi-stage cyclic analysis. It also shows how to use the cyclic support for advanced postprocessing
from ansys.dpf import core as dpf
from ansys.dpf.core import examples, operators as ops
Create the model and display the state of the result.
cyc = examples.download_multi_stage_cyclic_result()
model = dpf.Model(cyc)
print(model)
DPF Model
------------------------------
Modal analysis
Unit system: MKS: m, kg, N, s, V, A, degC
Physics Type: Mechanical
Available results:
- node_orientations: Nodal Node Euler Angles
- displacement: Nodal Displacement
- stress: ElementalNodal Stress
- elastic_strain: ElementalNodal Strain
- elastic_strain_eqv: ElementalNodal Strain eqv
- element_orientations: ElementalNodal Element Euler Angles
- structural_temperature: ElementalNodal Structural temperature
------------------------------
DPF Meshed Region:
3595 nodes
1557 elements
Unit: m
With solid (3D) elements
------------------------------
DPF Time/Freq Support:
Number of sets: 6
Cumulative Frequency (Hz) LoadStep Substep Harmonic index
1 188.385357 1 1 0.000000
2 325.126418 1 2 0.000000
3 595.320548 1 3 0.000000
4 638.189511 1 4 0.000000
5 775.669703 1 5 0.000000
6 928.278013 1 6 0.000000
Check the result info to verify that it’s a multi-stage model
result_info = model.metadata.result_info
print(result_info.has_cyclic)
print(result_info.cyclic_symmetry_type)
True
multi_stage
Go over the cyclic support
cyc_support = result_info.cyclic_support
print("num stages:", cyc_support.num_stages)
print("num_sectors stage 0:", cyc_support.num_sectors(0))
print("num_sectors stage 1:", cyc_support.num_sectors(1))
print(
"num nodes in the first stage's base sector: ",
len(cyc_support.base_nodes_scoping(0)),
)
num stages: 2
num_sectors stage 0: 6
num_sectors stage 1: 12
num nodes in the first stage's base sector: 2220
Expand displacement results#
This example expands displacement results on chosen sectors.
# Create displacement cyclic operator
UCyc = dpf.operators.result.displacement()
UCyc.inputs.data_sources(model.metadata.data_sources)
# Select the sectors to expand on the first stage
UCyc.inputs.sectors_to_expand([0, 1, 2])
UCyc.inputs.read_cyclic(2)
# Or select the sectors to expand stage by stage
sectors_scopings = dpf.ScopingsContainer()
sectors_scopings.labels = ["stage"]
sectors_scopings.add_scoping({"stage": 0}, dpf.Scoping(ids=[0, 1, 2]))
sectors_scopings.add_scoping({"stage": 1}, dpf.Scoping(ids=[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]))
UCyc.inputs.sectors_to_expand(sectors_scopings)
# expand the displacements and get a total deformation
nrm = dpf.Operator("norm_fc")
nrm.inputs.connect(UCyc.outputs)
fields = nrm.outputs.fields_container()
# # get the expanded mesh
mesh_provider = model.metadata.mesh_provider
mesh_provider.inputs.read_cyclic(2)
mesh = mesh_provider.outputs.mesh()
Plot the expanded result on the expanded mesh#
mesh.plot(fields)
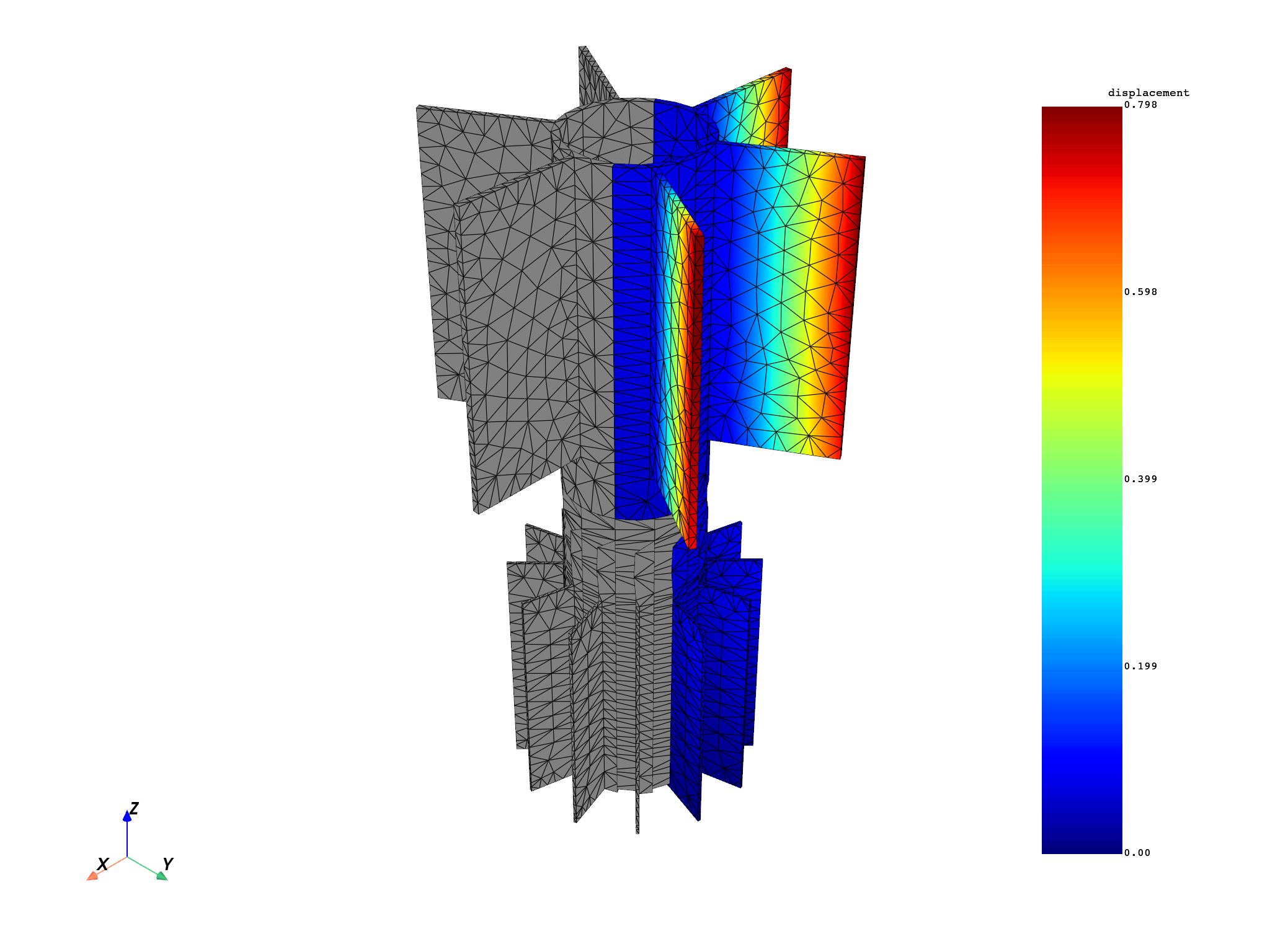
(None, <pyvista.plotting.plotter.Plotter object at 0x0000024EF9DD7850>)
Choose to expand only some sectors for the mesh#
cyc_support_provider = ops.metadata.cyclic_support_provider(
data_sources=model.metadata.data_sources
)
cyc_support_provider.inputs.sectors_to_expand(sectors_scopings)
mesh_exp = ops.metadata.cyclic_mesh_expansion(cyclic_support=cyc_support_provider)
selected_sectors_mesh = mesh_exp.outputs.meshed_region()
# # plot the expanded result on the expanded mesh
selected_sectors_mesh.plot(fields)
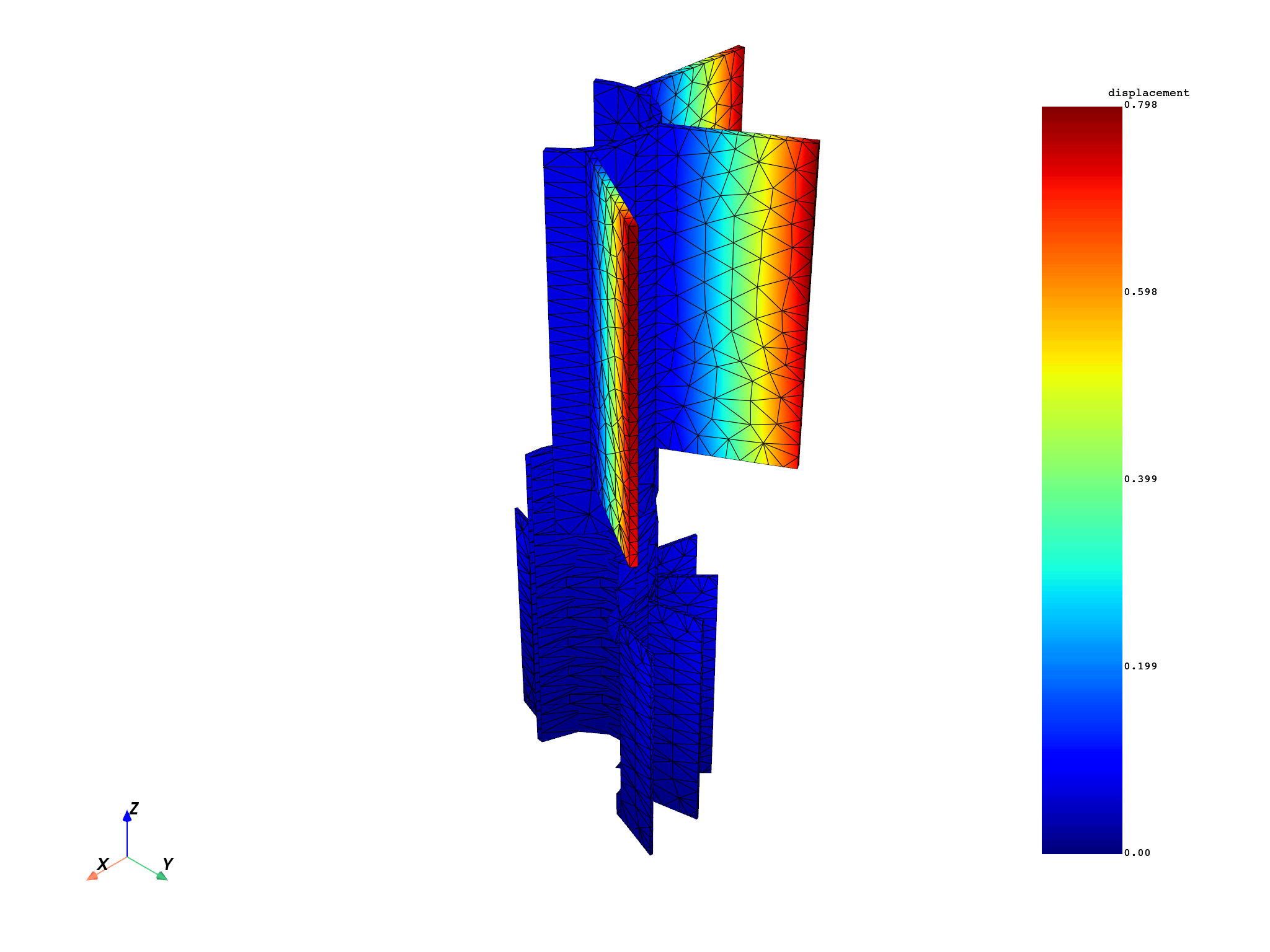
(None, <pyvista.plotting.plotter.Plotter object at 0x0000024EF98595D0>)
Check results precisely#
# Print the time_freq_support to see the harmonic index
print(model.metadata.time_freq_support)
print(model.metadata.time_freq_support.get_harmonic_indices(stage_num=1).data)
# Harmonic index 0 means that the results are symmetric sectors by sector
# taking a node in the base sector of the first stage
node_id = cyc_support.base_nodes_scoping(0)[18]
print(node_id)
# Check what are the expanded ids of this node
expanded_ids = cyc_support.expand_node_id(node_id, [0, 1, 2], 0)
print(expanded_ids.ids)
# Verify that the displacement values are the same on all those nodes
for node in expanded_ids.ids:
print(fields[0].get_entity_data_by_id(node))
DPF Time/Freq Support:
Number of sets: 6
Cumulative Frequency (Hz) LoadStep Substep Harmonic index
1 188.385357 1 1 0.000000
2 325.126418 1 2 0.000000
3 595.320548 1 3 0.000000
4 638.189511 1 4 0.000000
5 775.669703 1 5 0.000000
6 928.278013 1 6 0.000000
[0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.]
1394
[1394 4989 7209]
[0.07179672]
[0.07179672]
[0.07179672]
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 2.481 seconds)

