Getting started#
The Data Processing Framework (DPF) provides numerical simulation users and engineers with a toolbox for accessing and transforming simulation data. DPF can access data from Ansys solver result (RST) files as well as from several neutral file formats, including CSV, HDF5, and VTK. This workflow-based framework allows you to perform complex preprocessing and postprocessing operations on large amounts of simulation data.
PyDPF-Core is a Python client API communicating with a DPF Server, either through the network using gRPC or directly in the same process.
Install PyDPF-Core#
To install PyDPF-Core, in a Python environment, run this command:
pip install ansys-dpf-core
For more installation options, see Installation section.
Install DPF Server#
DPF Server is packaged within the Ansys installer in Ansys 2021 R1 and later. To use it, download the standard installation using your preferred distribution channel, and install Ansys following the installer instructions. If you experience problems, see Environment variable. For information on getting a licensed copy of Ansys, visit the Ansys website.
DPF Server is available as a standalone package (independent of the Ansys installer) on the DPF Pre-Release page of the Ansys Customer Portal. As explained in Ansys licensing, DPF Server is protected by an Ansys license mechanism. Once you have access to an Ansys license, install DPF Server:
Download the
ansys_dpf_server_win_v2023.2.pre1.ziporansys_dpf_server_lin_v2023.2.pre1.zipfile as appropriate.- Unzip the package and go to its root folder (
ansys_dpf_server_win_v2023.2.pre1or ansys_dpf_server_lin_v2023.2.pre1).
- Unzip the package and go to its root folder (
In a Python environment, run this command:
pip install -e .
DPF Server is protected using the license terms specified in the DPFPreviewLicenseAgreement file, which is available on the DPF Pre-Release page of the Ansys Customer Portal. To accept these terms, you must set this environment variable:
ANSYS_DPF_ACCEPT_LA=Y
For more information about the license terms, see DPF Preview License Agreement.
For installation methods that do not use pip, such as using Docker containers, see Getting started with DPF Server.
Use PyDPF-Core#
To use PyDPF-Core, in the same Python environment, run this command:
>>> from ansys.dpf import core as dpf
>>> from ansys.dpf.core import examples
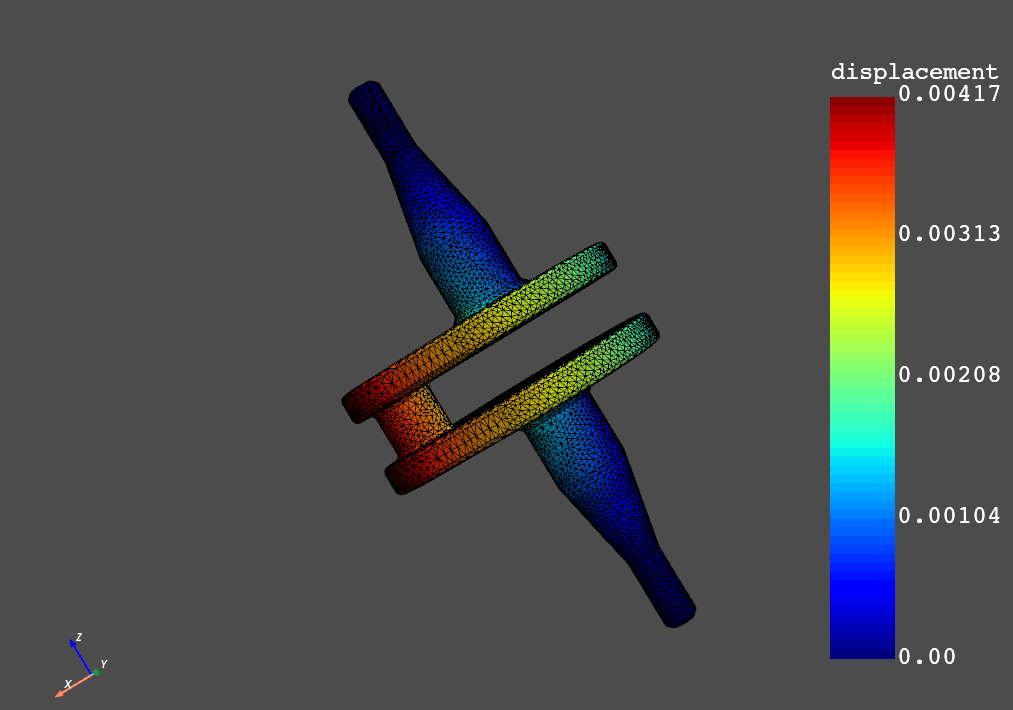
>>> model = dpf.Model(examples.download_crankshaft())
>>> print(model)
DPF Model
------------------------------
Static analysis
Unit system: MKS: m, kg, N, s, V, A, degC
Physics Type: Mechanical
Available results:
- displacement: Nodal Displacement
- velocity: Nodal Velocity
- acceleration: Nodal Acceleration
- reaction_force: Nodal Force
- stress: ElementalNodal Stress
- elemental_volume: Elemental Volume
- stiffness_matrix_energy: Elemental Energy-stiffness matrix
- artificial_hourglass_energy: Elemental Hourglass Energy
- thermal_dissipation_energy: Elemental thermal dissipation energy
- kinetic_energy: Elemental Kinetic Energy
- co_energy: Elemental co-energy
- incremental_energy: Elemental incremental energy
- elastic_strain: ElementalNodal Strain
- structural_temperature: ElementalNodal Temperature
------------------------------
DPF Meshed Region:
69762 nodes
39315 elements
Unit: m
With solid (3D) elements
------------------------------
DPF Time/Freq Support:
Number of sets: 3
Cumulative Time (s) LoadStep Substep
1 1.000000 1 1
2 2.000000 1 2
3 3.000000 1 3
>>> over_time_disp = model.results.displacement().eval()
>>> over_time_disp[0].plot()